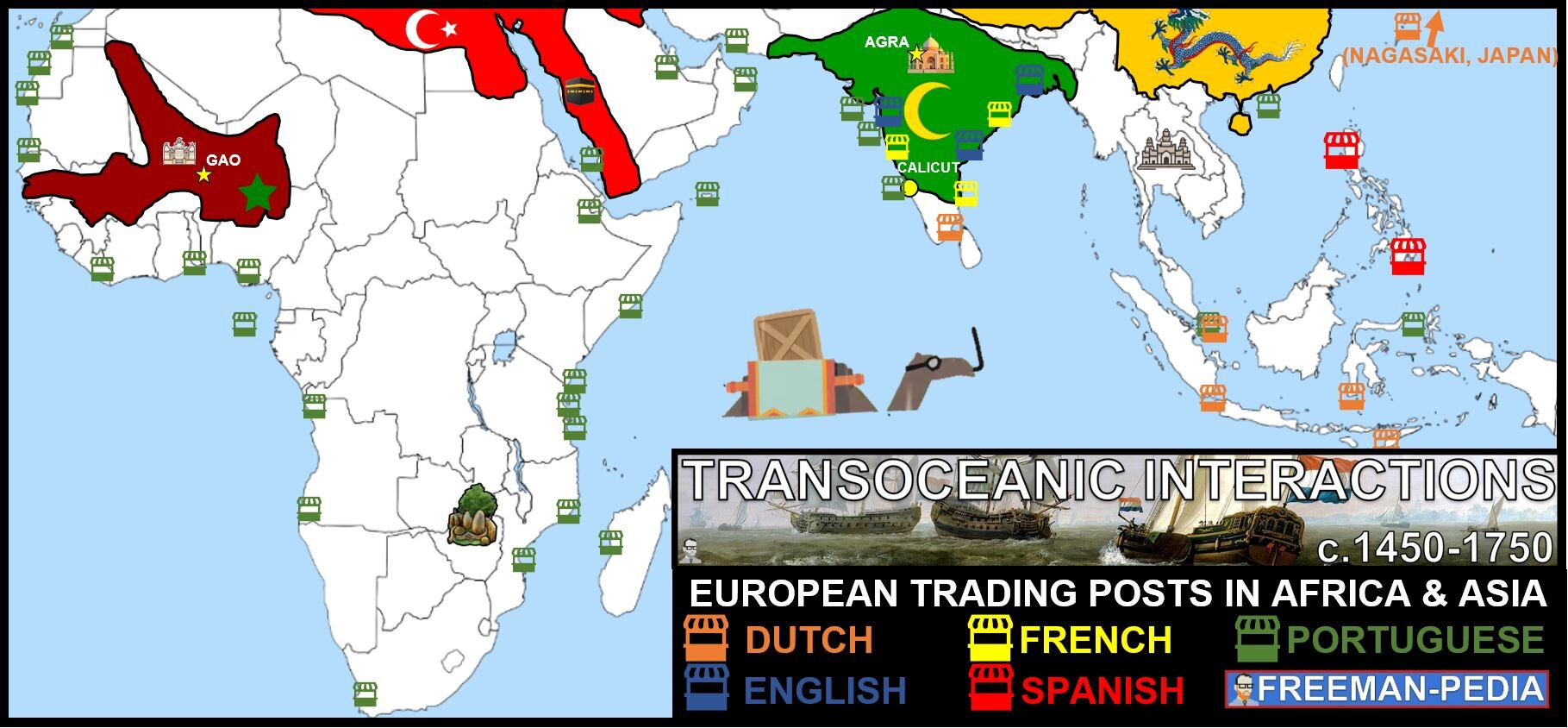
As Europe sets off to expand across the oceans, the first contestant=PORTUGAL. Check out a map. They are super far away from any trade route. Not isolated, but but out there. So, it makes sense that they would lead the way in seeking out new trade routes and peoples to convert to Catholicism. Portugal has a decent head start as well. King John the Good (Henry’s dad) first took territory in Africa (Ceuta) in 1415! Columbus was 77 years later. That’s a massive lead in terms of exploration. Everyone else took their cues from Portugal in the sea route to Asia. Having said that… Portugal’s empire will not be the largest (Britain) or the longest lasting (Ottomans). . They have their crown jewel: BRAZIL; but otherwise, they are pretty much a Trading Post Empire without significant land holdings outside of Brazil (The Portuguese are the 21st largest empire ever, just behind the Achaemenid Persians). So, when studying the Portuguese; remember them for their explorers, and being the first Europeans to reach a lot of places by sea… This is the Portuguese Empire:
HENRY the NAVIGATOR
COLUMBUS vs. ZHENGHE vs. DA GAMA
VASCO DA GAMA from the HISTORY CHANNEL
HOW MAGELLAN CIRCUMNAVIGATED THE GLOBE via TEDED
CRASH COURSE EUROPEAN HISTORY: EXPLORATION
THE TRANSATLANTIC SLAVE TRADE
PORTUGUESE RULE OVER BRAZIL